Oct 1, 2025 | 6 minutes
Make + Vapi - a powerful combination for Conversational AI
For Make customers using the Vapi voice agent platform, it’s now easier than ever to implement Custom Tools that integrate with your existing tech stack. David Gurr explains what’s changed and how you can benefit.
Background
Conversational AI agent builders like Vapi have the potential to change the Agentic AI landscape, changing the default interface from chat to voice.
A phone is the universal API. What better way to increase the reach of your service than to allow your users to speak with an AI assistant, rather than type? To deliver on that promise effectively, Conversational AI platforms need to address three key challenges:
Latency - significant delays in speech processing can make the conversation sound unnatural
Accuracy - errors in understanding from digitized speech can destroy the illusion of speaking with a helpful assistant
Integration - increasingly, customers are demanding conversational access to the systems-of-record they already have in use - their CRMs, ERPs, finance/accounting systems, HR systems, and others.
Vapi, like others in the Conversational AI space, is an expert in facing the first two challenges. But how can you effectively address the third when there are literally thousands of solutions that your customers might be using? That’s where Make comes in.
Make delivers access to over 3,000 SaaS solutions through pre-built connectors (or “apps” in our terminology), including popular and niche systems-of-record: CRMs, ERPs, finance and accounting systems, HR systems, project management, identity management, IT help desks, and marketing automation systems.
The role of tools in agentic systems
Tools are essential for agentic AI systems because they enable the agents to overcome their limitations. While large language models (LLMs) can generate text and reason about information they've learned, they are essentially confined to the knowledge they were trained on. They can't access up-to-date information, perform actions outside of their internal processes, or connect with other systems in a user’s tech stack.
Tools provide the agent with a crucial link to its environment. This allows an AI agent to perform tasks such as looking up a customer’s status in a CRM, raising an invoice, or updating a project management system - things an LLM alone can't do. In essence, tools act as the agent's hands and eyes, allowing it to perceive its environment, gather new data, and execute actions to achieve a specific goal.
Difficulties in building tools
While agentic AI platform vendors like Vapi include built-in tools for the most common use-cases - such as booking a calendar appointment or sending a Slack message - tools for other use-cases must be created specifically.
Agentic tools are usually implemented through REST API requests to a Webhook endpoint. Traditionally, those endpoints and their back-end code would be hosted as a serverless function on services such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions or Google Cloud Functions.
But that requires skilled developers, both for initial development and ongoing maintenance. Additionally, building connections to system-of-record platforms like CRMs and ERPs can involve a lot of logistical overhead.
No-code workflow automation platforms like Make provide a much easier route. With thousands of pre-built apps for systems-of-record, builders can create tools that access business systems with ease. What’s more, tools built using Make can be maintained and enhanced by non-technical staff. You don’t need to be constrained anymore by the availability of development resources.
Options for creating custom tools for Vapi using Make
Original Webhook method
Vapi Custom Tools require a backend that handles a Webhook request with optional parameters, responding with a well-defined response structure to return information to the Agent.
Make’s Custom Webhook and Webhook Response modules can be used to implement this. There are several steps to follow:
Create a scenario in Make with just a Custom Webhook module and leave it “listening” for the data structure
Create a Custom Tool definition in Vapi with any required parameters and include that Tool in an Assistant definition
Run the Assistant to send a test request to the Make scenario
The Custom Webhook recognizes the parameters and makes them available for the following scenario modules
Build out the rest of the Make scenario, ending with a Transform to JSON module and Webhook Response module to return the parameters
2. MCP
Apart from Custom Tools, Vapi also provides a mechanism for using tools offered by MCP Servers.
The Make MCP Server provides selected Make scenarios as tools for AI Agents, including Vapi, Make AI Agents, and other agentic platforms.
If you already have a set of tools available through Make on-demand scenarios and want to leverage the same resources for Vapi, check the Make MCP documentation for details.
3. New Vapi Watch Tool Call Request and Respond to a Tool Call modules
While the original Webhook method works well, it can be a little tricky to set up. In the latest version of the Vapi app on Make, we’ve put more effort into making that easier.
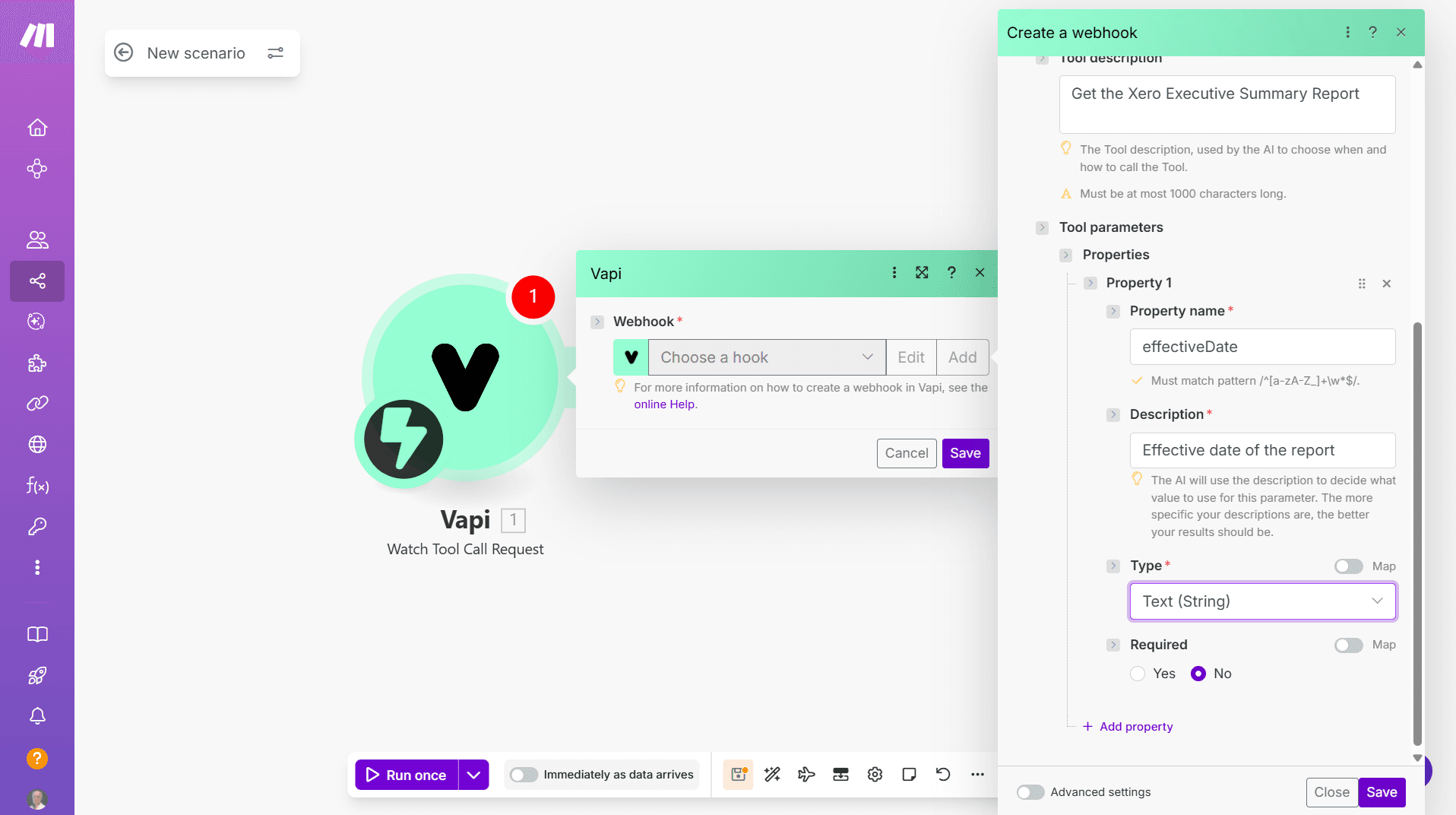
The new Watch Tool Call Request module allows you to create both the Webhook and the entire Vapi Custom Tool definition from within Make. This means that you don’t need to switch between Make and Vapi environments, copying and pasting each time.
To make changes once the tool has been created, you’ll need to manage it within the Vapi dashboard.
You can add Tool Parameters:
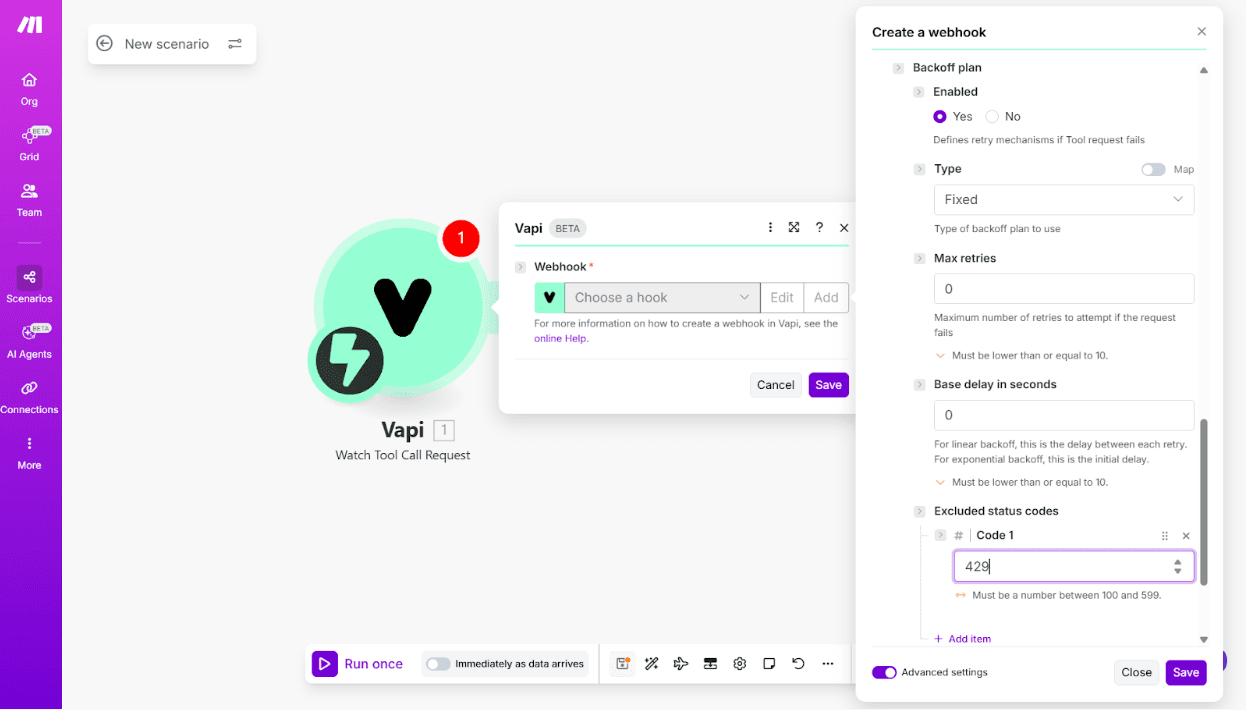
And even add advanced parameters such as a Backoff plan:
To make changes once the tool has been created, you’ll need to manage it within the Vapi dashboard.
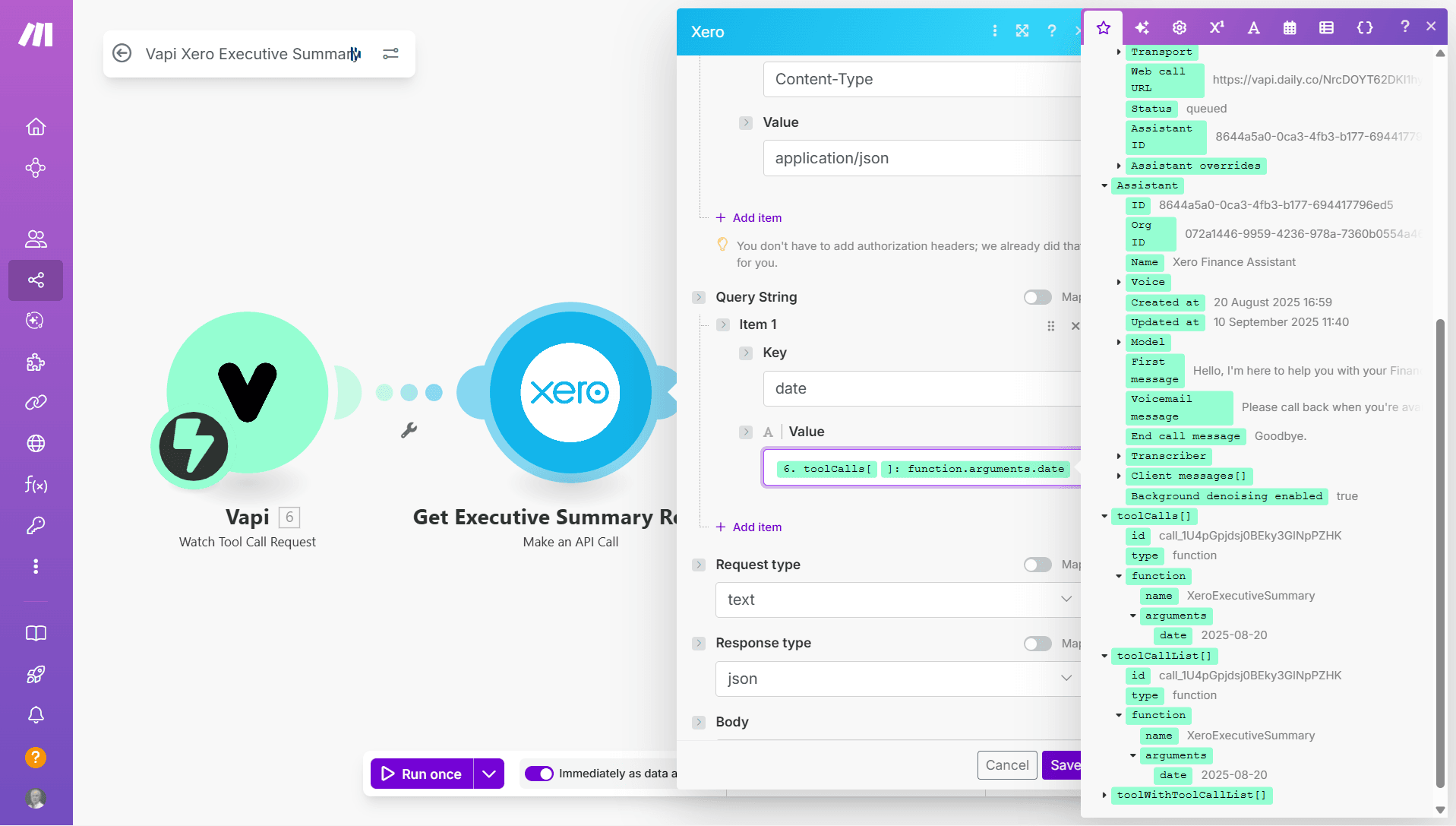
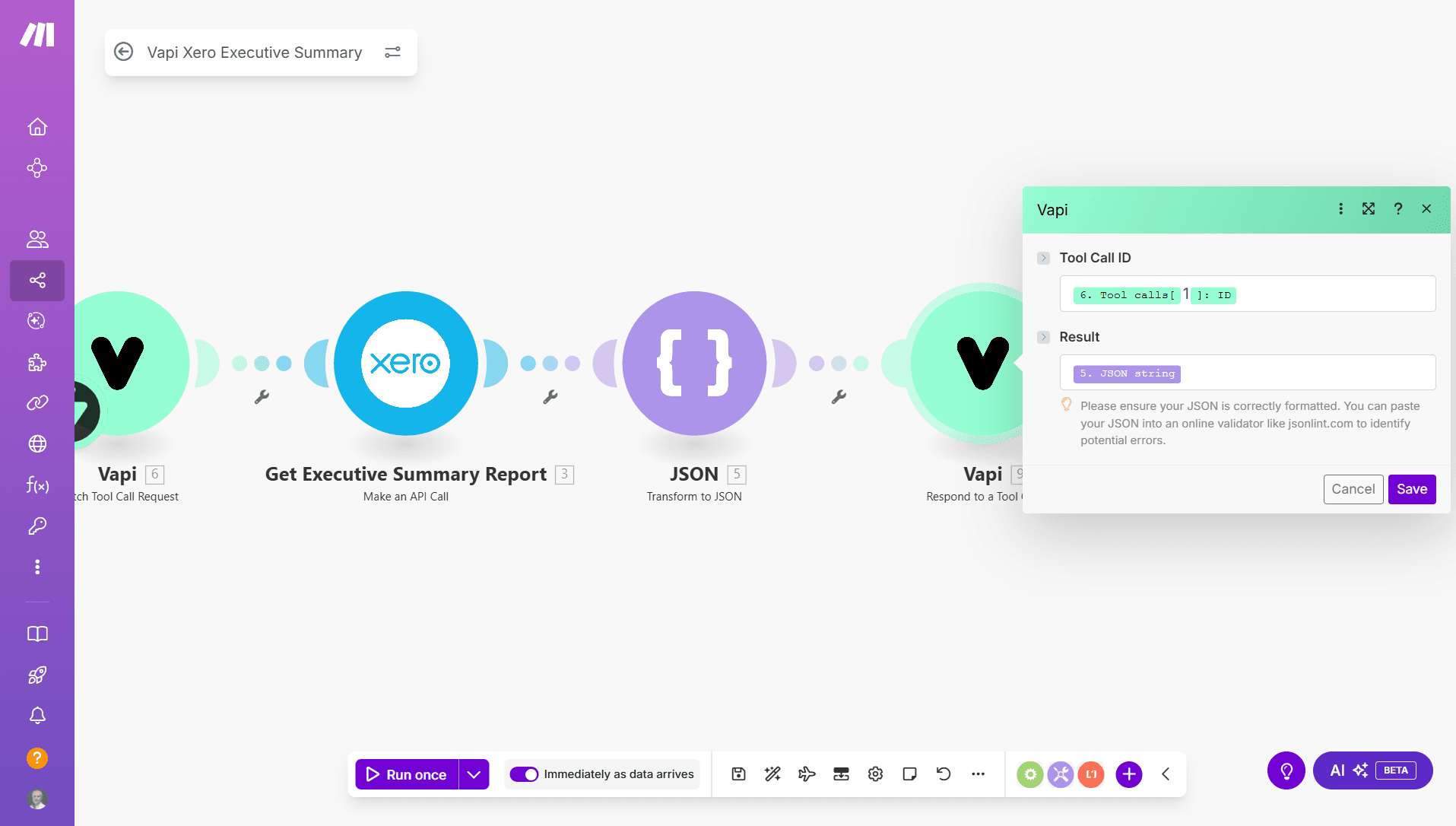
Accessing tool parameters in the following modules is simple - they’re automatically available under toolCalls[].function.arguments as shown in the screenshot below:
For example:
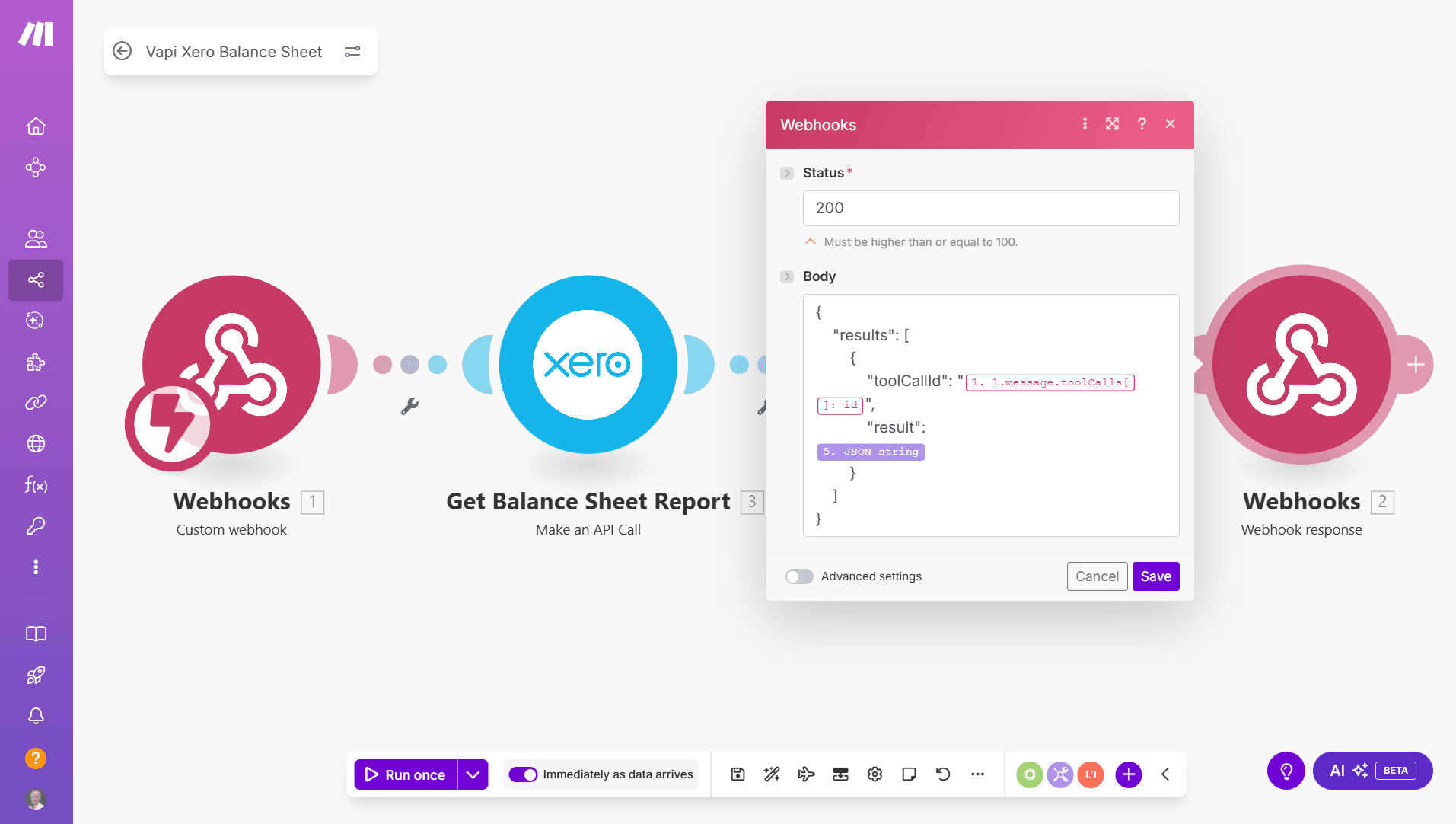
The other tricky part of the original Webhook mechanism is in providing the response packet.
We’ve also simplified that. The new Respond to a Tool Call module takes just two arguments - the Tool Call ID that’s returned from the Watch Tool Call Request module, and a string for the response:
Conclusion
The combination of Vapi and Make delivers a powerful solution for integrating conversational AI with a user's existing systems.
The new Watch Tool Call Request and Respond to a Tool Call modules simplify the process of creating tools for Vapi. These new modules eliminate the need to switch between platforms, making it easier for users to create and manage custom tool definitions, access parameters, and format responses, all from within Make. This enhanced integration addresses the third major challenge of conversational AI - connecting with a vast number of different systems - and empowers businesses to more effectively leverage their existing technology with a voice-activated AI assistant.