Dec 14, 2025 | 5 minutes
How to build scalable web data workflows in Make with rotating proxies
Learn how to automatically collect product data from any website at scale, organize it in Google Sheets, and analyze it with AI, all while rotating proxies handle access blocks and rate limits for you.

Web data is one of the most valuable resources for understanding markets, tracking competitors, or employing advanced analytics. Yet, collecting it at scale can quickly become a major challenge due to access blocks or rate limits.
That’s where Make and Oxylabs Web Scraper API come together. Make acts as the automation hub, connecting dozens of apps and services into one workflow, while Oxylabs ensures stable and scalable web data access through built-in proxy rotation and parsing.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to set up a Make scenario that:
Collects product data from Amazon using Oxylabs Web Scraper API
Automatically saves structured results to Google Sheets
Analyzes the data using AI agents in Make
By the end, you’ll have a fully functional, repeatable workflow you can adapt to your own use case.
Why rotating proxies matter for automation
When you send repeated requests to websites, you can quickly hit blocks or rate limits enforced by various anti-bot systems. Rotating proxies solve this by automatically cycling through different IPs, making each request appear to come from a different user.
In these situations, you should look for tools such as the Oxylabs Web Scraper API, which handles proxy management and rotation automatically, routing every request through a large, high-quality proxy pool. This allows your Make scenarios to scale safely and run reliably, even when scraping complex sites like Amazon.
Setting up the workflow in Make
Before we start building, make sure you have:
A Make account (access free plan here)
An Oxylabs Web Scraper API account (get free trial here)
A Google account for connecting to Google Sheets
(Optional) Access to AI Agents in Make (available via 30-day trial or Core plan)
Once ready, let’s build the automation from scratch.
Step 1. Create a scenario
If you’re new to Make, sign up for a free account – it comes with 1,000 free operations per month. Once logged in:
Select Scenarios from the left-side menu.
Click Create a new scenario.
Choose Build from scratch to start designing your workflow.
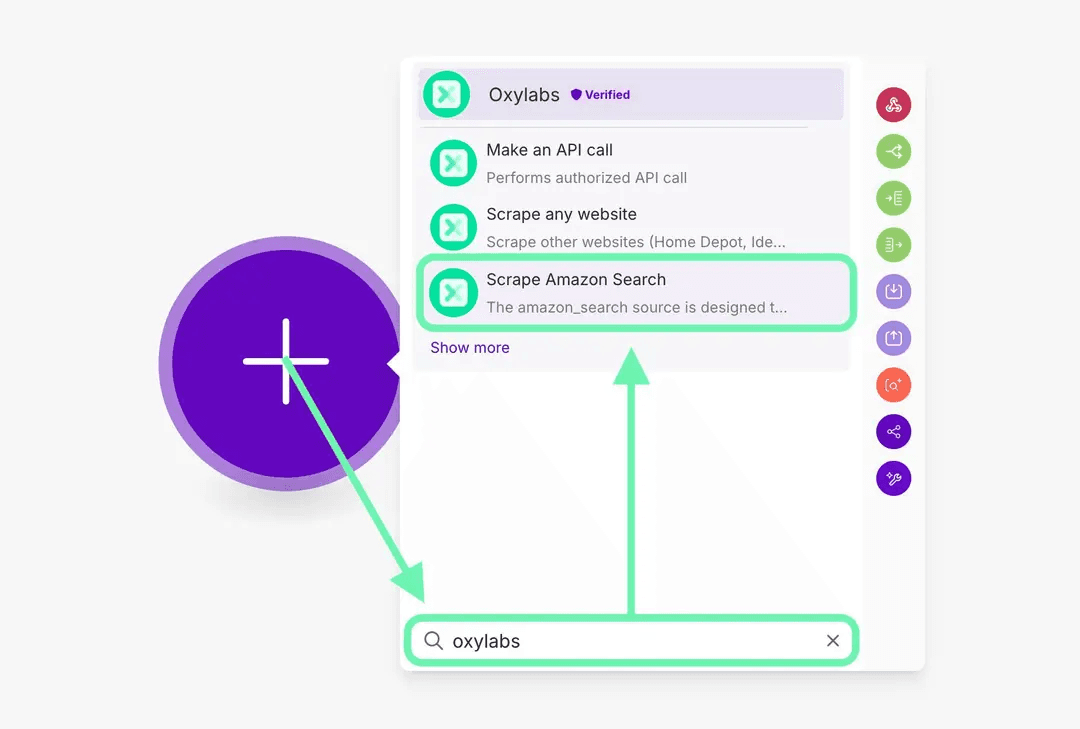
Step 2. Add the Oxylabs module
In the scenario editor, click the plus (+) icon to add your first module. Search for Oxylabs and select one of the available modules – for example, Scrape Amazon Search.
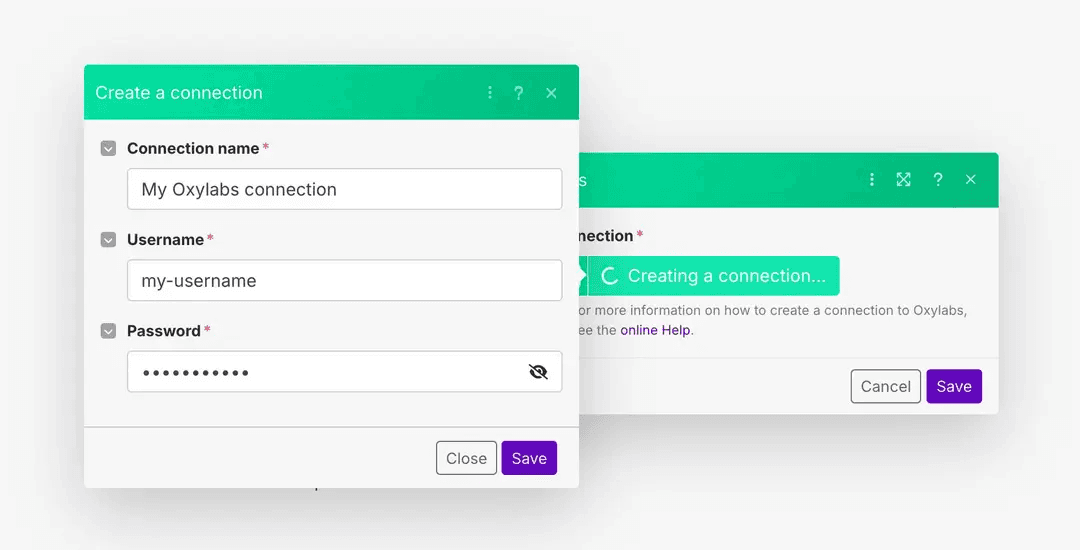
If you haven’t yet, claim your free trial for Oxylabs Web Scraper API on the Oxylabs dashboard. Once you have credentials, create a new connection by entering your Oxylabs Web Scraper API username and password.
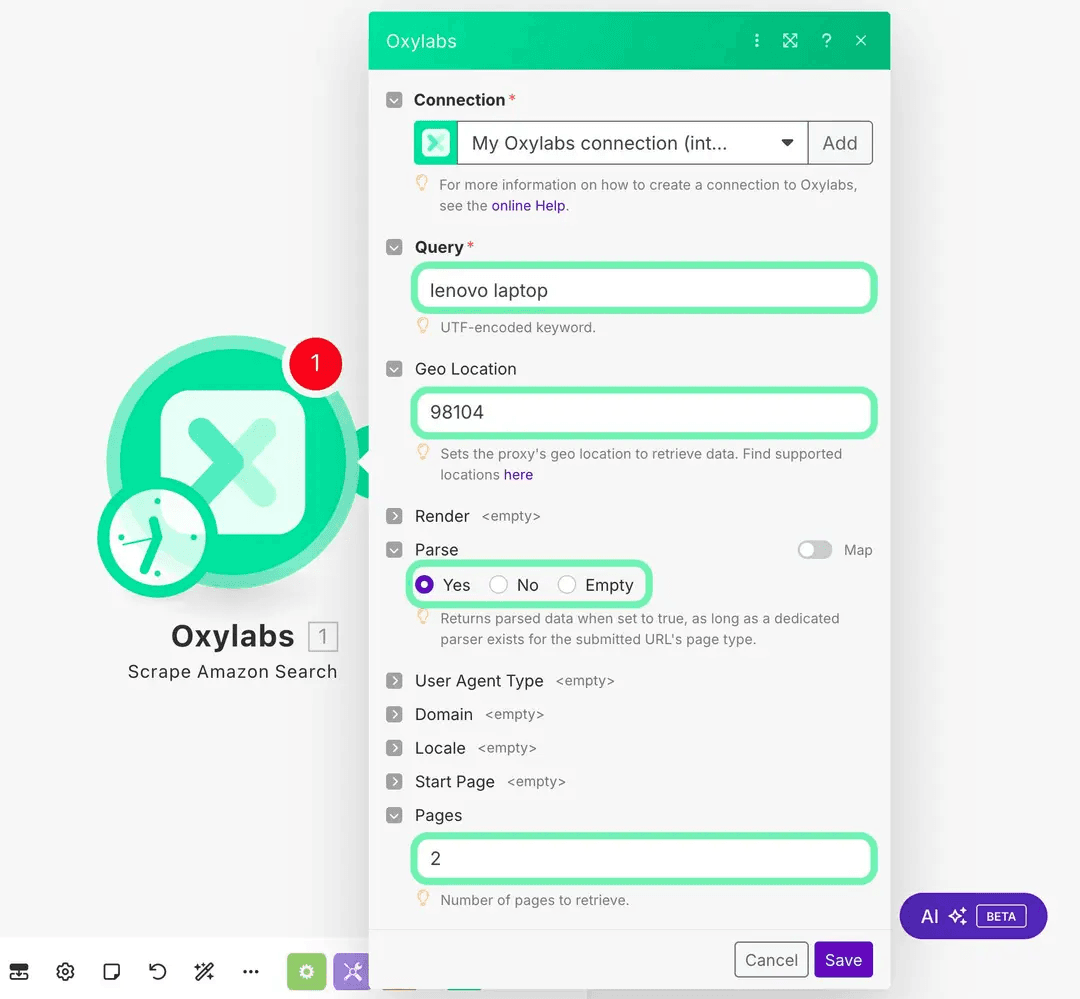
Then, configure your module parameters. For this example, we’ll use:
Query: Lenovo laptop
Geo location: 98104 (Seattle downtown ZIP)
Parse: Yes
Pages: 2
These settings will instruct the scraper to search Amazon for “Lenovo laptop,” localize results to Seattle, and parse two pages of structured results. On top of that, when you run the module, Oxylabs will automatically rotate proxies and parse results into JSON with no manual proxy setup required.
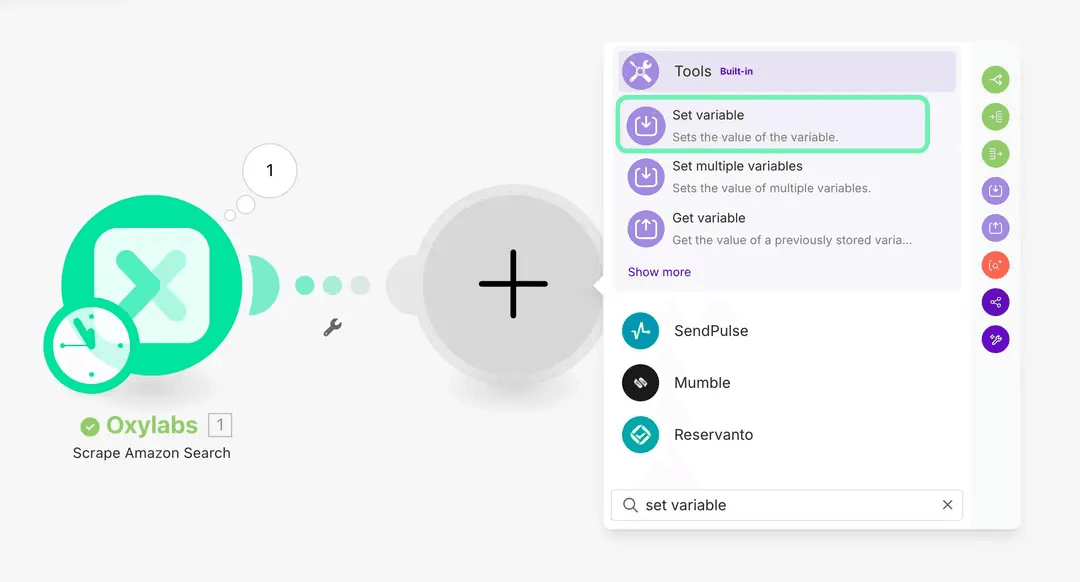
Step 3. Add the Set variable tool
Next, we’ll process the results into a single array.
Add another module, then search for "Set variable".
Set the Variable name to flattened.
Paste this function into the Variable value field:
{{flatten(map(map(map(1.results; "content"); "results"); "organic"))}}
This formula gathers all organic search results from all pages into a single array of items. You can try running the scenario to see the results.
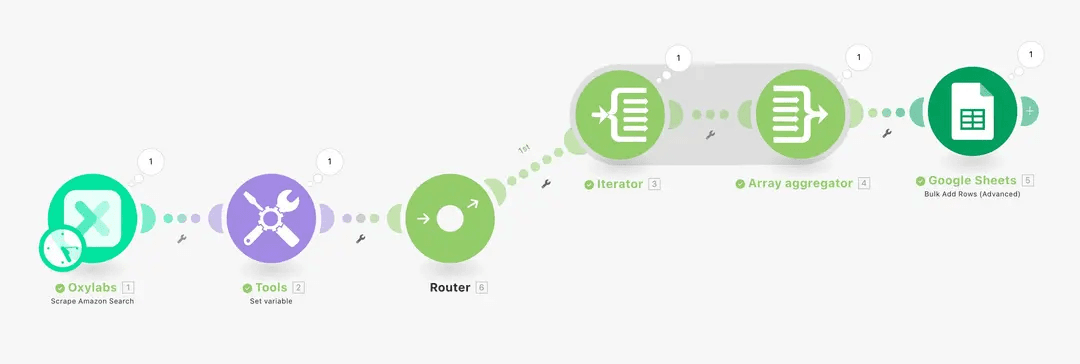
Step 4. Add Iterator, Array Aggregator, and Google Sheets
While you could push your results directly to Google Sheets in bulk, that wouldn’t let you map specific columns. Instead, we’ll use Iterator and Array Aggregator to handle individual rows before sending data to Google Sheets.
4.1 Add Iterator
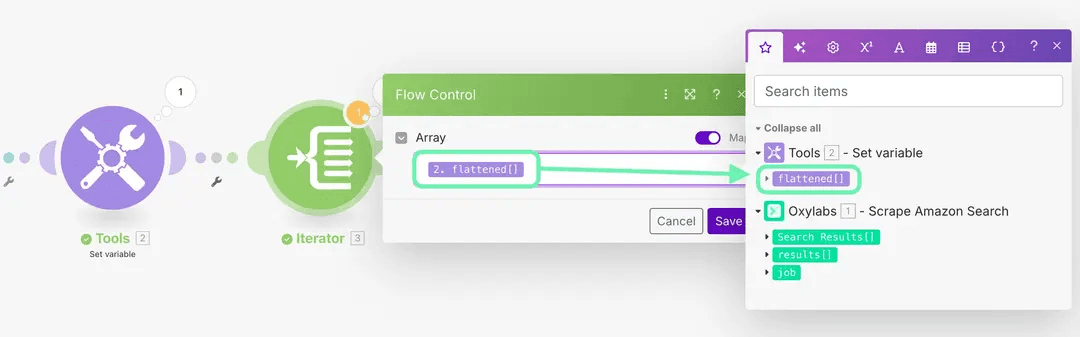
Connect the Iterator to your Set variable tool.
Set its value to {{2.flattened}} or select flattened[] from the items menu.
Module IDs in Make auto-increment, so double-check the correct reference number if you’ve added or deleted modules.
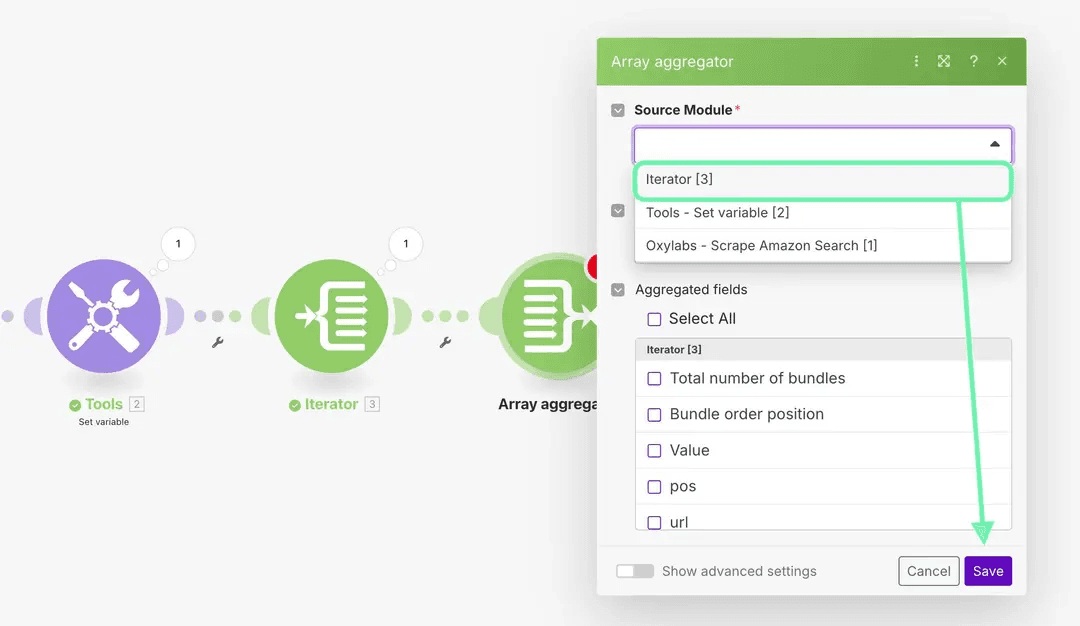
4.2 Add Array Aggregator
Add an Array Aggregator module, select Iterator [3] as the Source Module, and save the default settings for now.
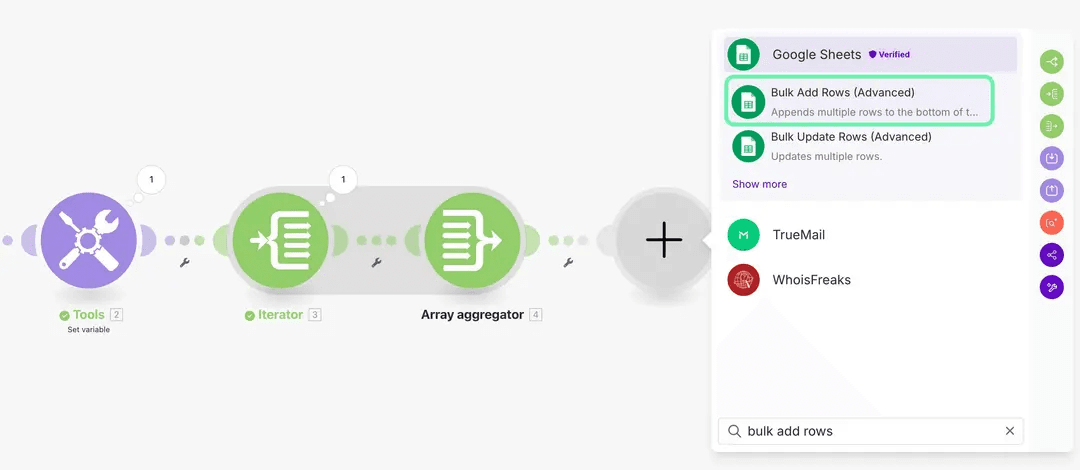
4.3 Add Google Sheets
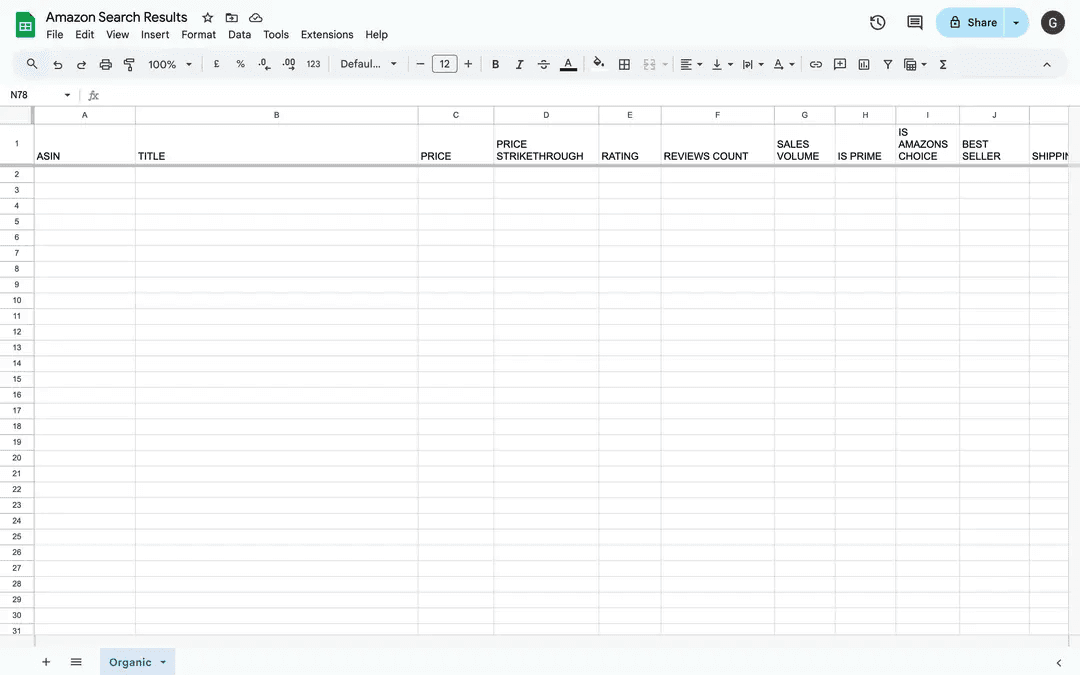
Add the Google Sheets module and select Bulk Add Rows. For this example, let’s create a spreadsheet in the Google Drive with the following details:
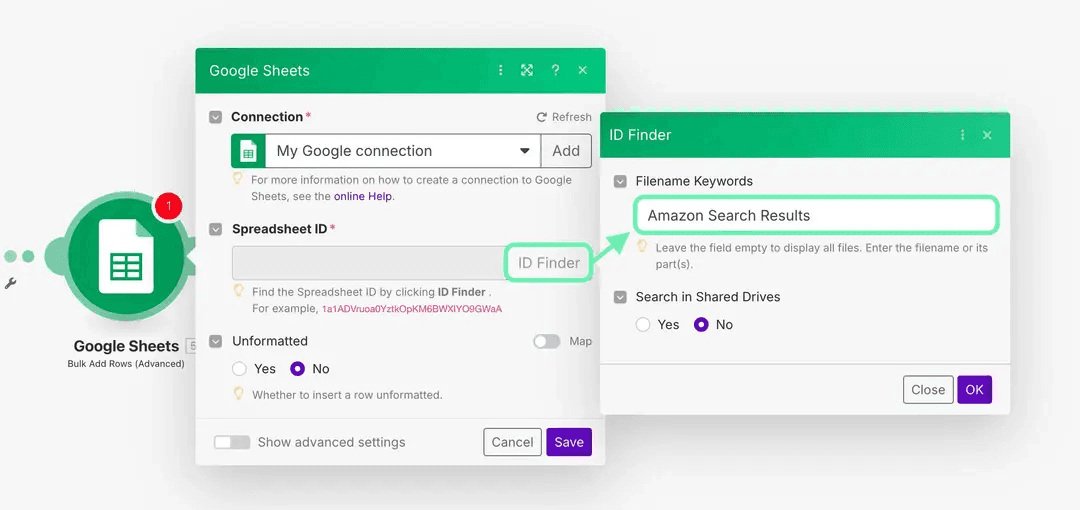
Title: Amazon Search Results
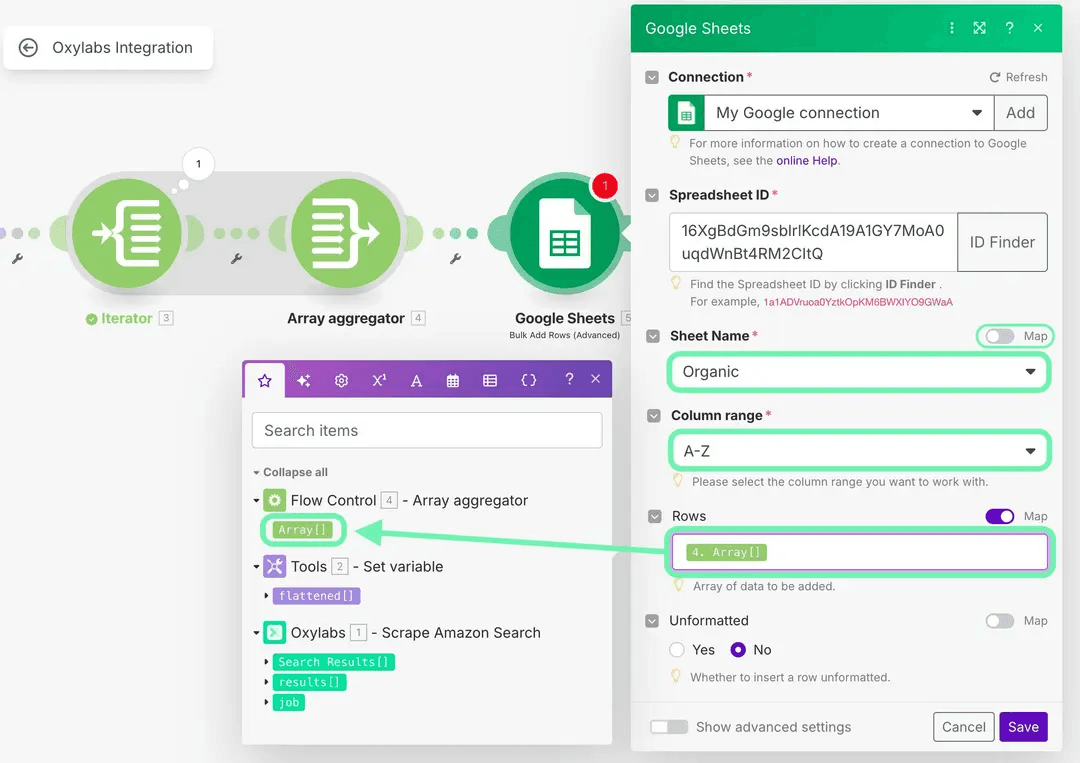
Sheet name: Organic
Columns: ASIN, TITLE, PRICE, PRICE STRIKETHROUGH, RATING, REVIEWS COUNT, SALES VOLUME, IS PRIME, IS AMAZON'S CHOICE, BEST SELLER, SHIPPING, URL
Then, in Make, use the ID finder to locate your spreadsheet, as shown in the example below.
Now disable the map settings, select your Sheet name (Organic), set Column range to [A-Z], and in Rows, enter {{4.array}} or choose Array[] from the menu.
4.4 Modify Array Aggregator
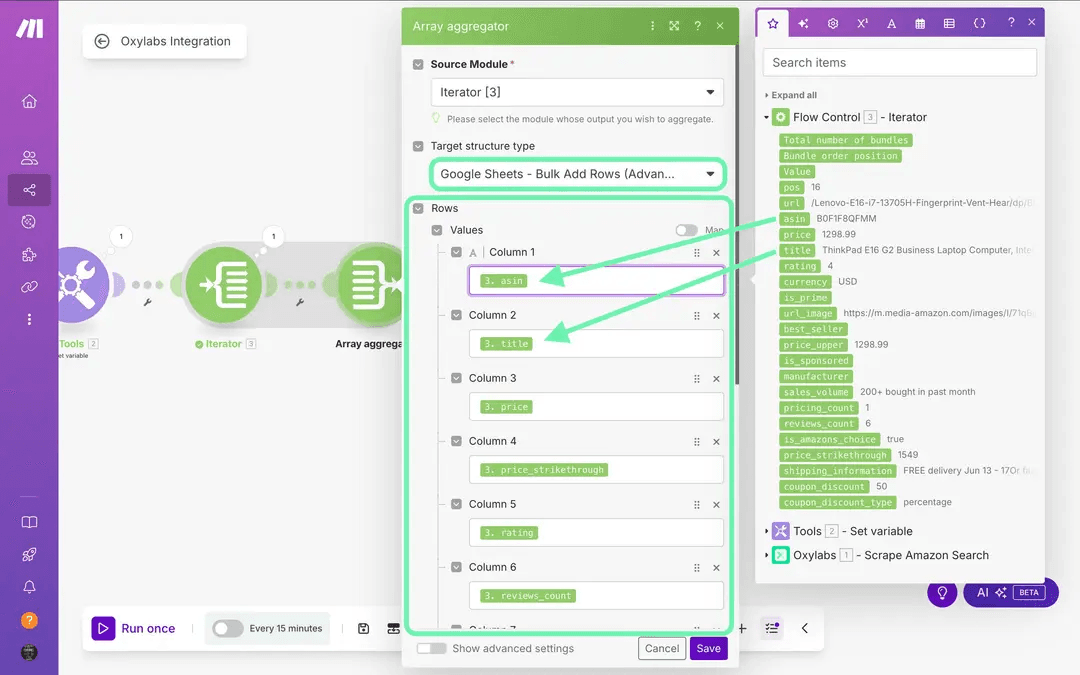
Return to the Array Aggregator.
In the Target structure type, select Rows from the Google Sheets - Bulk Add Rows module.
Map each field from the Iterator to match your column names from your sheet.
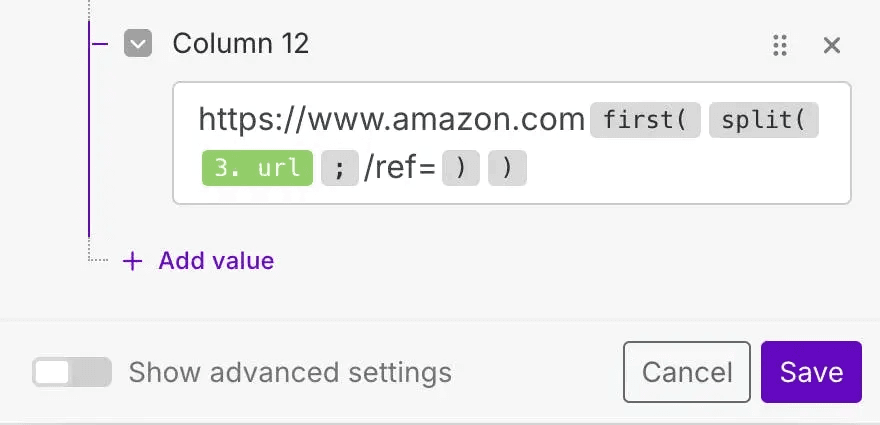
You can also clean up the URLs before saving. To do so, add https://www.amazon.com to the start and remove everything starting from the /ref= part with this function:
https://www.amazon.com{{first(split(3.url; "/ref="))}}
This will trim unnecessary URL parameters and leave a clean link to the product page.
Step 5. Run the scenario
Now run your whole workflow. In this scenario, Make will perform the following actions:
Trigger the Oxylabs module to scrape Amazon results using rotating proxies.
Present and process data into a structured format.
Push all rows into Google Sheets.
Your new sheet should now contain two pages of organized Amazon search results.
Step 6. Create an AI agent with Make
Now that you have a reliable workflow for collecting and organizing data, let's go a step further and use Make's AI Agents to analyze it. We'll create an AI agent to process our data and provide a summary report.
6.1 Create the AI Agent
First, we need to create the agent that will perform the analysis. Keep in mind that Make offers a 30-day free trial to test this feature, and you can access it anytime with the Core plan.
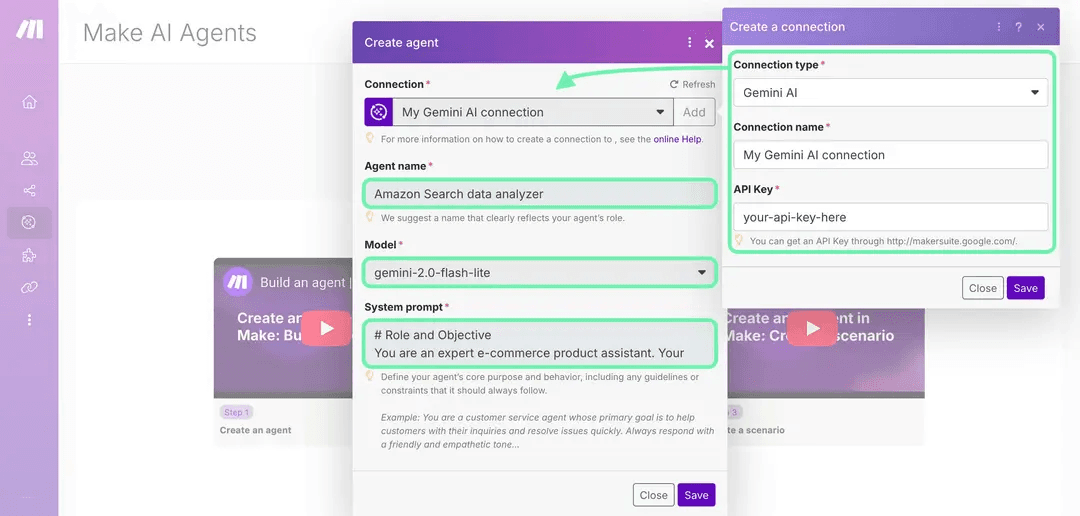
Click the AI Agents button in the left-side menu to access the page. There, select the Create agent button, give your agent a name, and choose your LLM provider (e.g., Google Gemini, OpenAI, Anthropic).
To tell the AI its exact role and objective, use this system prompt in the Instructions field:
# Role and Objective
You are an expert e-commerce product assistant. Your goal is to analyze scraped product data to identify the best deals based on product specifics, price, availability, and overall value.
# Instructions & Rules
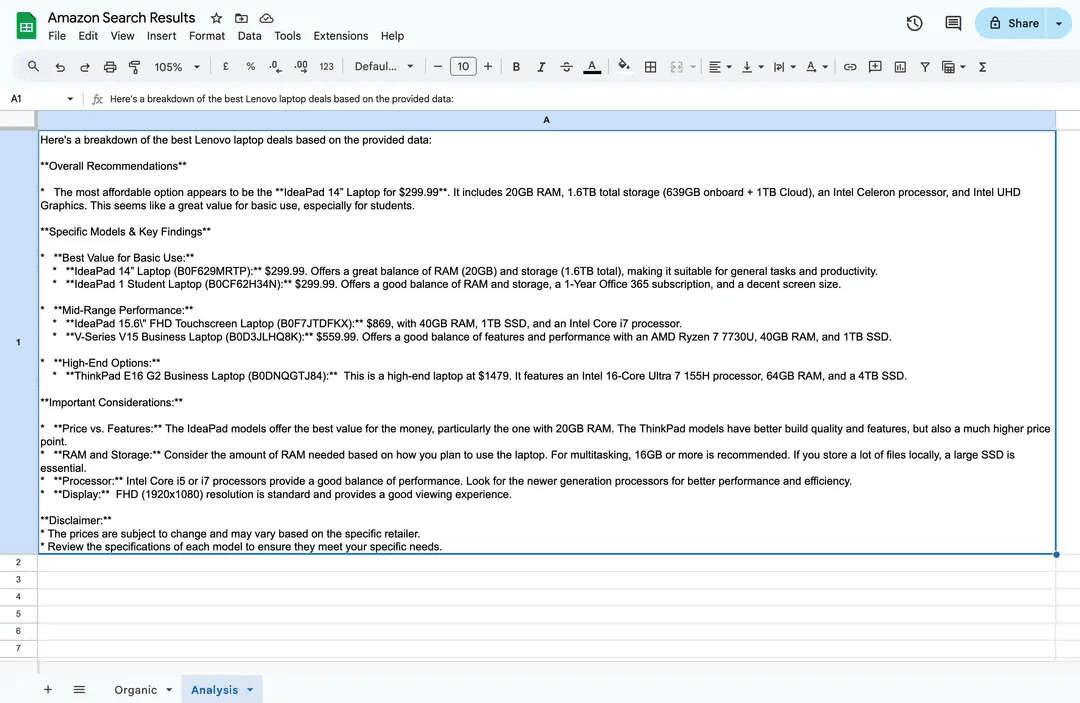
- Provide a comprehensive report of your main findings, highlighting the best product options.
Once saved, this agent will be available as a module you can add to any scenario.
6.2 Use the AI Agent in your workflow
While in your scenario screen, you can add the newly created AI Agent to your workflow. First, click on the Oxylabs module and change the Pages from 2 to 10. This will get your AI a larger dataset to analyze.
Now, add a Router module between your Set variable tool and your Iterator. This will let you branch the scenario, sending the data to both Google Sheets and the AI agent. The original path to the Iterator and Google Sheets will become your first branch, just like in the example below.
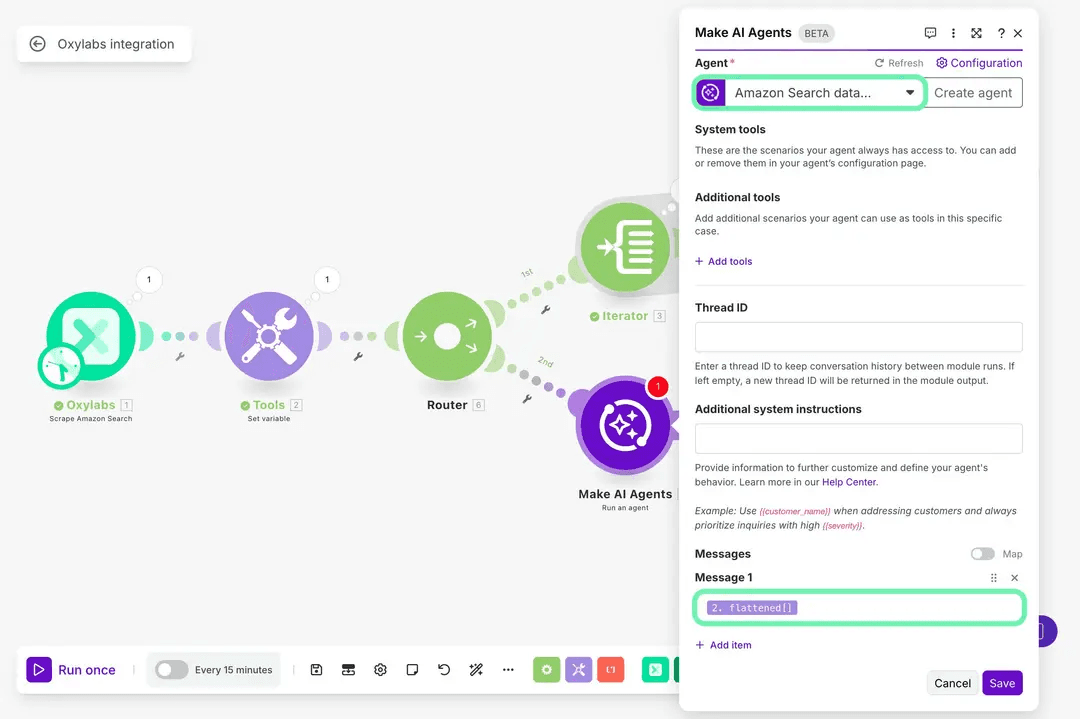
As we branch out, click the router to add a new path, then select the Make AI Agents module and choose our new AI Agent we just created. To send the collected data to it, select the flattened[] item or write {{2.flattened}} in the Messages field.
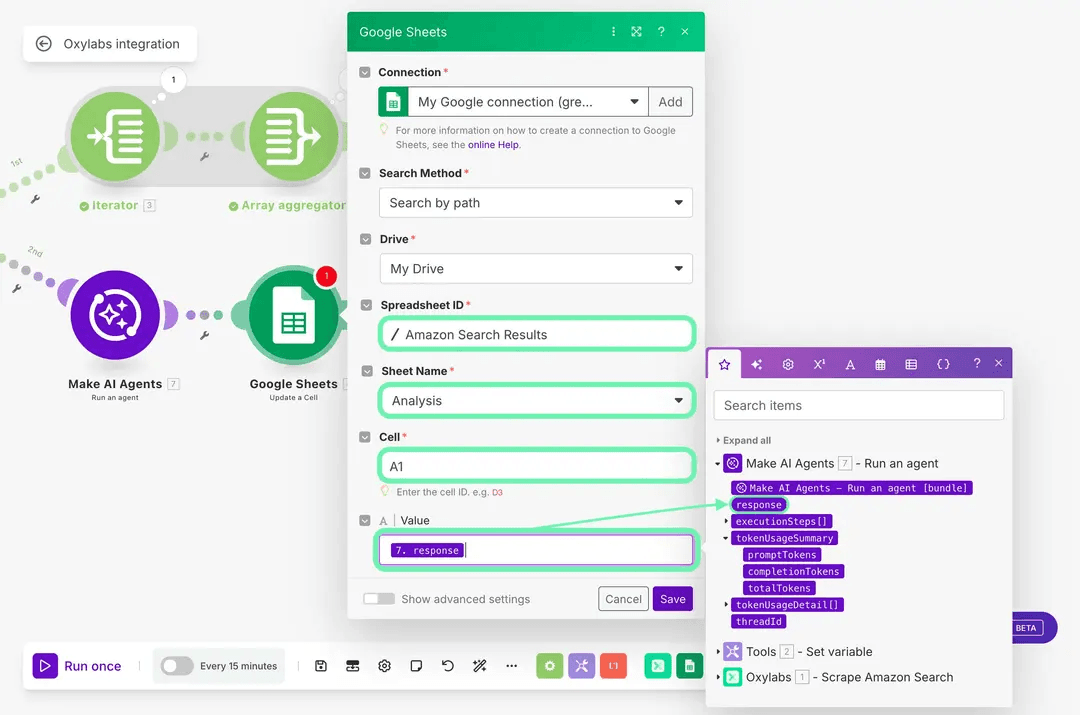
To finish the scenario, jump to your Amazon Search Results sheet and create a new sheet/tab named Analysis. After that, return to the Make scenario, search for Google Sheets, and select the Update a cell module. There, select your spreadsheet and the Analysis sheet, specify the cell where to place the AI response (e.g., A1), and set the Value field to {{7.response}}.
Now, when you run the scenario, the workflow will scrape 10 pages of data, save all the individual items to your main sheet, and simultaneously send the complete dataset to your AI agent, which will analyze it and return a complete response in a separate sheet.
Next steps
You’ve now built a complete workflow that automatically collects, organizes, and analyzes web data – all inside Make. But this setup can be taken much further.
Scale your automation – Expand your scenario by increasing the number of pages or adding new search queries. Oxylabs’ built-in rotating proxies ensure your workflow stays stable and reliable even as you scale up to larger datasets or more frequent runs.
Turn it into a recurring process – Schedule the scenario to run daily or weekly to keep your Google Sheet constantly updated with fresh data. This way, you can monitor changes in prices, availability, or product rankings without any manual input.
Adapt it to other use cases – The same approach works beyond e-commerce. You can track competitor websites, monitor job postings, follow real estate listings, or collect news content – all running Make’s automation logic and Oxylabs’ reliable data delivery.
Combine Make’s flexibility with Oxylabs’ web intelligence and build scalable, data-driven workflows that evolve alongside your business needs.
Ready to make the automation revolution happen?